
Project Overview
Since carbon recycling that leverages biomanufacturing technology can be expected to greatly improve productivity in the future due to the application of cutting-edge bio technologies such as genome editing and genome construction, it is a viable option for helping realize a carbon neutral society.
Biomanufacturing refers to activities for producing chemicals used in bioplastics, functional materials, fuels, and foods (such as protein and livestock feed) using CO2 recovered from biomass resources and the atmosphere as a raw material. In the industrial sector in Japan, biomanufacturing-related industries such as chemicals, textiles, and food/beverages discharge 89.017 million tons of CO2 per year, and biomanufacturing technologies can be expected to help reduce CO2 emissions.
Through promoting joint development efforts between microorganism modification platform businesses, who play a central role in biomanufacturing, and businesses in a variety of fields such as innovative materials and fuels, this project aims to nurture and strengthen operating companies that will drive large-scale fermentation and biomanufacturing production. Moreover, by leveraging the technologies of platform businesses related to the highly efficient development of microorganisms, the inherent capacity of microorganisms to fixate CO2 will be fully maximized with a view to resolving technical issues and promoting carbon recycling through biomanufacturing that uses CO2 as a raw material. In addition, by constructing a value chain ranging from the supply of CO2 raw materials to the manufacturing of products, and by promoting upscaled commercial production and more sophisticated manufacturing technologies, the project aims to realize both the social application of new biomanufacturing products made from CO2 raw materials and the structural transformation of the industrial sector through carbon recycling.
Project Features
〇 R&D item 1
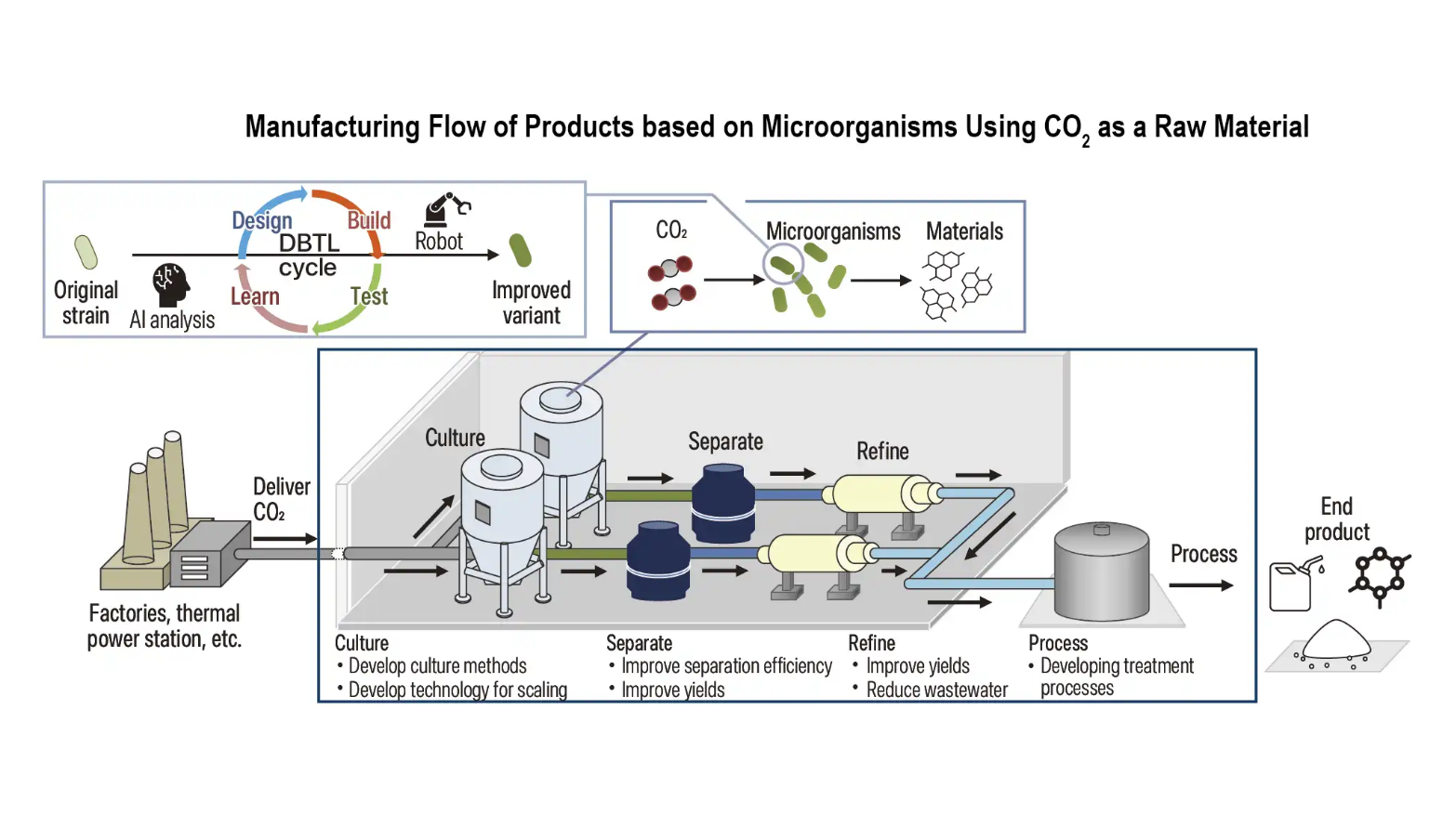
Sophistication of microorganisms and modification of platform for accelerating the development of useful microorganisms
Through supporting the development of microorganism modification platform technologies integrating bio base technologies, digital technologies such as IT and AI, and automation technologies such as robotics, the project aims to speed up the design, build, test, learn (DBTL) cycle with a view to expanding the range of useful microorganisms capable of efficiently absorbing and fixating CO2 used for producing materials, and reducing the time and costs incurred in the modification process.
〇 R&D item 2
Development and enhancement of microorganisms that can produce materials using CO2 as raw material
Through promoting joint development between microorganism modification platform businesses, who play a central role in biomanufacturing, and businesses in a variety of fields such as innovative materials and fuels, microorganism variants will be developed whose metabolic pathways for producing materials have been optimized for enhanced productivity.
〇 R&D item 3
Development and demonstration of technologies using microorganisms that can produce materials using CO2 as raw material
For the production of materials that use CO2 as a raw material, a new method for culturing microorganism variants using carbon raw materials and reducing power will be developed. Moreover, to realize commercial applications for the produced materials, processing technologies and quality assessment methods will be developed with final products in mind. Furthermore, when demonstrating the production of such materials, lifecycle assessment (LCA) methods and methods for standardizing quantitative assessments of fixated CO2 will also be developed.