
Project Overview
The power sector is moving toward decarbonization by introducing renewable energy to the greatest extent possible. However, in order to meet domestic demand for electricity, it is necessary to maintain a certain amount of thermal power generation and capture the resulting CO2 emissions.
At the same time, while efforts to realize decarbonization in the industrial sector are moving forward, by such means as electrification and fuel conversion to hydrogen, demand for fossil fuels is expected to continue to some degree due to cost-related factors. In addition, it is difficult to avoid CO2 emissions emanating from raw materials used in industrial sectors such as cement, steel, and chemicals.
There is consequently an increasing need for CO2 separation and capture technologies in both the power generation and industrial sectors. However, challenges include the large amount of energy inputs needed for separation and capture and high costs for the equipment and materials used for capture.
The aims of this project are to establish technology for the first time for low-pressure, low-concentration CO2 separation and capture at a concentration of 10% or less, to expand the business for CO2 separation and capture equipment and materials, and to strengthen Japan's international competitiveness in the carbon recycling market while linking these results to the development of negative emission technologies such as Direct Air Capture (DAC).
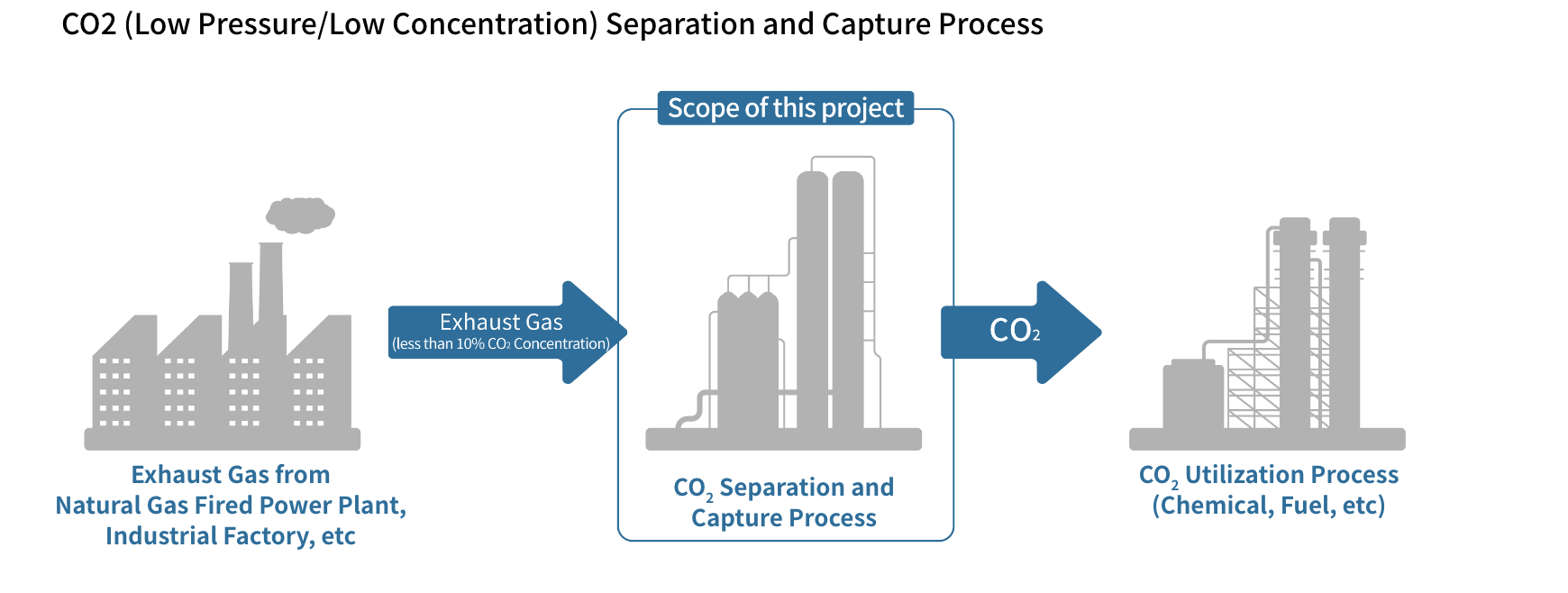
Project Features
〇 Technology development and demonstration of large-scale CO2 separation and capture from natural gas-fired power generation exhaust gas
Targeting exhaust gas from large-scale natural gas-fired power generation, achieve technology for realizing CO2 separation and capture costs of 2,000 yen level (less than 3,000 yen) per ton by 2030. Confirm realization of the project targets via demonstrations at plants using actual gas (10 tons/day or more).
〇 Technology development and demonstration of small- and medium-scale CO2 separation and capture from factory exhaust gas, etc.
Targeting exhaust gas from cogeneration systems, boilers, heat-treatment furnaces, and naphtha-cracking furnaces, achieve technology for realizing CO2 separation and capture costs of2,000 yen level (less than 3,000 yen) per ton by 2030. Confirm realization of the project targets via demonstrations at plants using actual gas (0.5 tons/day or more).
〇 Establish a common base for evaluating the standards of CO2 separation materials
To accelerate the development of CO2 separation materials for low-pressure and low-concentration exhaust gas, establish a base for evaluating the standards of CO2 separation and capture using actual gas. Specifically, (1) establish a collaborative system between material manufacturers and engineering companies to acquire and collect data, (2) formulate standard performance evaluation methods using standard gas and actual gas, (3) develop a method for evaluating CO2 separation and capture costs through, for example, system analysis using data obtained from standard evaluation methods, (4) develop a method for evaluating durability using an accelerated aging system and simulation technology, and (5) consider how best to promote international standardization of the evaluation methods developed in activities (2) to (4).