
Project Overview
Carbon Recycling is a key technology that effectively utilizes CO2 as a resource for realizing a carbon neutral society. Japan has a competitive edge in the field of CO2 separation and capture, as well as certain kinds of chemicals relevant to this technology.
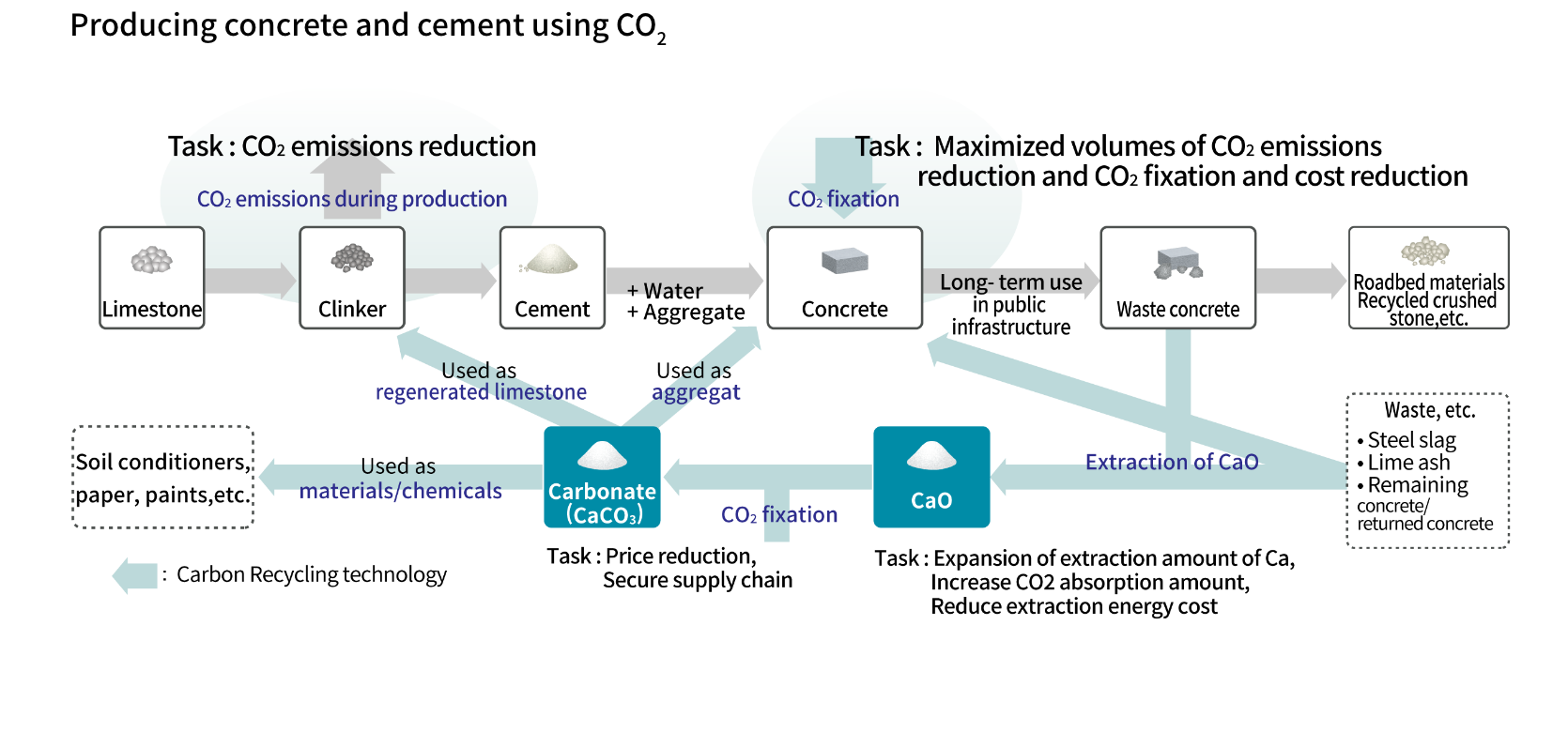
Due to the high potential for CO2 fixation and the stability of products, the use of CO2 in concrete, cement, and carbonates (hereinafter referred to as “concrete and cement fields”) in particular will be implemented in society, which is expected to greatly reduce CO2 levels. In Japan, the United States, and Europe, R&D and demonstration projects in this area are already underway.
In order to achieve decarbonization in this field, however, it is necessary to reduce CO2 emissions and increase CO2 fixation of concrete, a product used all around the world, as well as promote its use by reducing costs. Cement, a material used in concrete, also emits CO2 through the decarbonization reaction of limestone, one of its raw materials, making it another issue that needs to be addressed.
To realize a carbon neutral society, the aim of this project is to address the above issues related to the social implementation of Carbon Recycling technologies, and strategically promote their diffusion in Japan and overseas.
Project Features
〇 Development of concrete produced with maximized volumes of CO2 emissions reduction and CO2 fixation
The aim of this project is by 2030 to achieve maximized levels of CO2 emissions reduction and CO2 fixation during the production and transportation of materials, as well as establish a manufacturing system for concrete produced with maximized volumes of CO2 emissions reduction and CO2 fixation that realizes costs that are less than or equal to those of existing products.
〇 Development of technology related to quality control/fixation evaluation methods for concrete produced with maximized volumes of CO2 emissions reduction and CO2 fixation
By 2030, quality control methods will be realized under this project for concrete produced with maximized levels of CO2 emissions reduction and CO2 fixation. International standardization will also be pursued.
〇 Design and demonstration of CO2-recovering cement production process
The aim of this project is by 2030 to realize a CO2-recovering cement production process capable of recovering nearly all the CO2 from limestone and achieve cost reductions equal to or greater than current CO2 recovery methods (e.g., chemical absorption, amine scrubbing).
〇 Establishment of carbonic acid chloride technology using various calcium sources
The aim of this project is by 2030 to realize technologies for efficiently and economically producing carbonates by recovering CO2 and waste, and then utilize these as raw materials for cement, along with formulating guidelines to ensure product quality.