
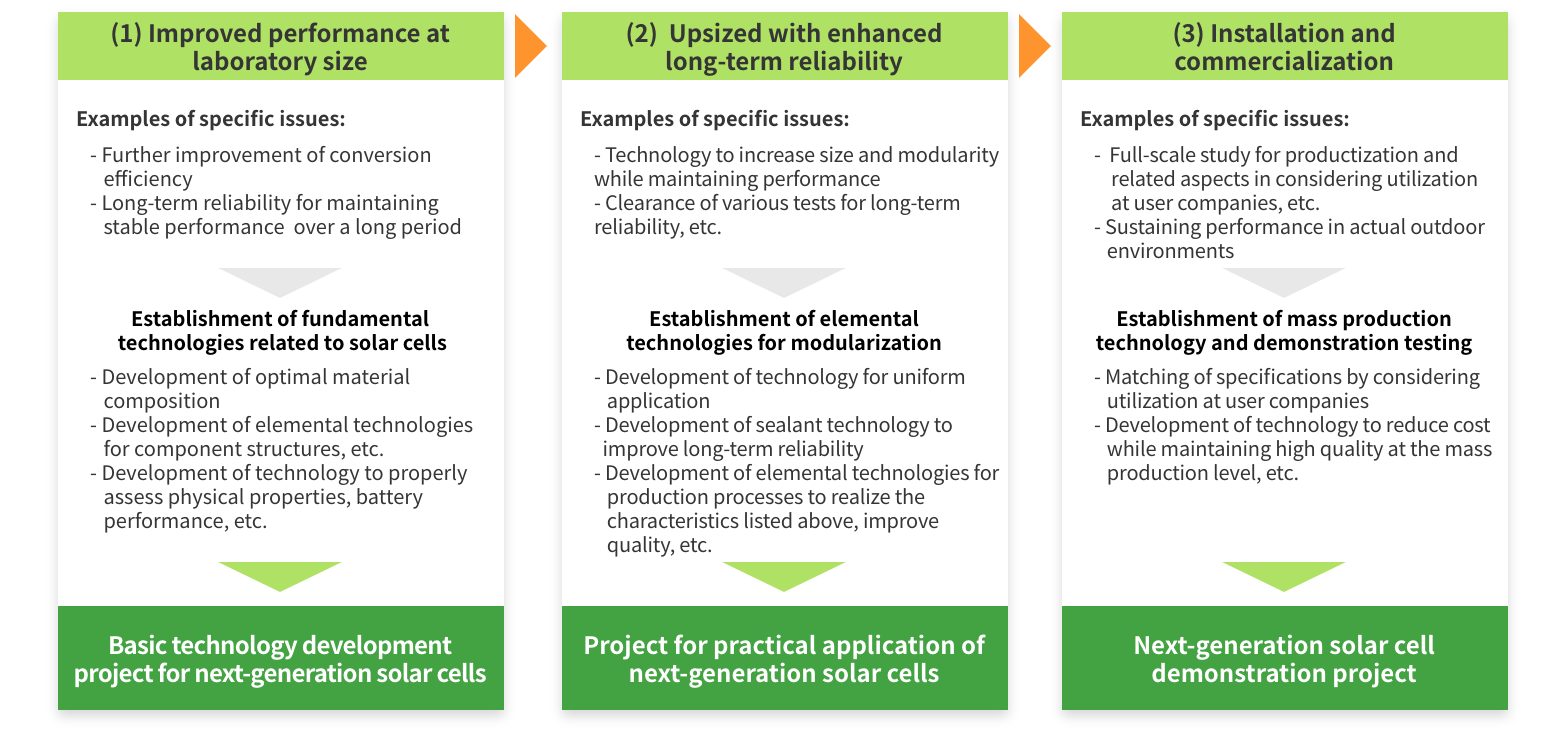
Project Overview
To achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, it is necessary to introduce renewable energy sources, including solar power, as much as possible with the aim of using them as primary sources of power. In Japan, where most land is not flat, one way of securing suitable areas for solar power generation is installing next-generation solar cells that can be installed in places where existing photovoltaic cells could not (walls of buildings, factory roofs that can only support small loads, etc.). Installation in such locations, therefore, requires the development of lightweight next-generation solar cells that are flexible enough to be installed on curved surfaces such as walls and which are also comparable to existing photovoltaic cells in terms of performance (conversion efficiency, long-term reliability, etc.).
Through the development of basic technologies for next-generation solar cells (perovskite solar cells) and R&D for realizing technologies for various manufacturing processes (coating processes, electrode formation, and sealing processes) for scaling up products, the aim of this project is to achieve the same electricity costs of 14 yen/kWh or less by 2030 as conventional silicon solar cells.
Project Features
〇 Basic technology development project for next-generation solar cells
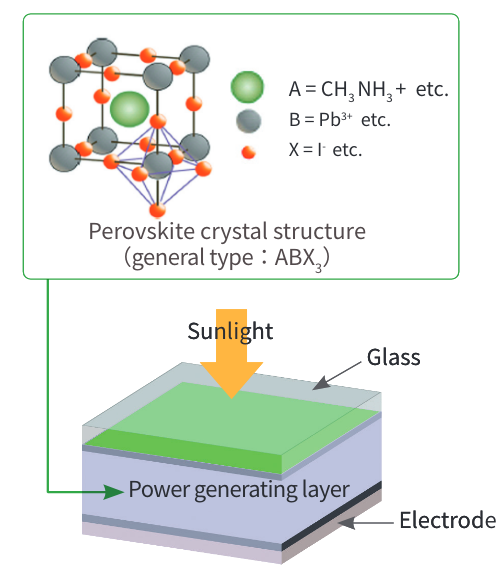
For perovskite solar cells, it is necessary to determine the optimum combination of raw materials from among tens of thousands of combinations, improve conversion efficiency, and improve durability for maintaining long-term performance. To create a market for such solar cell products, it is also necessary to develop and standardize methods for analyzing and evaluating battery performance and deterioration factors. R&D will therefore be carried out on the optimum material composition of perovskite solar cells, elemental technologies for batteries with high levels of conversion efficiency and durability, and analysis/evaluation techniques.
〇 Project for practical application of next-generation solar cells
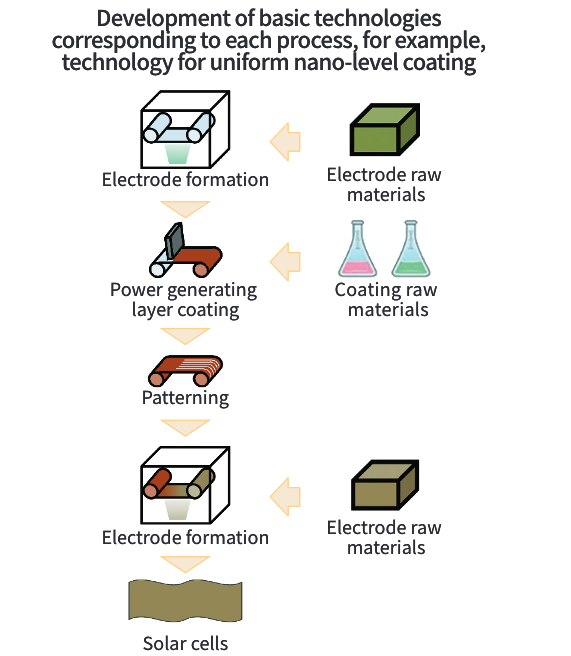
To realize perovskite solar cell modules that meet requirements related to the form of installation locations, conversion efficiency, durability, and power generation costs, in addition to utilizing basic technologies realized from the Basic technology development project for next-generation solar cells, R&D will be carried out for realizing elemental technologies for individual manufacturing processes (coating processes, electrode formation, and sealing processes) for scaling up products.
〇 Next-generation solar cell demonstration project

To realize technology that enables mass production and maintains stable levels of quality, technology will be developed to achieve high throughputs and yields as a series of linked production processes for each manufacturing process established in the project for practical application of next-generation solar cells. In order to verify performance, including installation and construction methods that utilize the lightness and flexibility of perovskite solar cells, field demonstrations will be conducted and improvements made in line with verification results.