
Project Overview
Industries in the food, agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector are expected to play multiple roles, including the provision of stable supplies of high-quality food, replenishment of the atmosphere and water sources, and promotion of biodiversity conservation through the appropriate management and conservation of croplands, forests, and oceans. Moreover, the amount of greenhouse gases captured and stored in areas such as croplands and forests reached 44.5 million tons in FY2020.
With a view to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries formulated its “Strategy for Sustainable Food Systems,” known as MeaDRI (Measures for Achievement of Decarbonization and Resilience with Innovation) in May 2021. This strategy clarifies Japanese government policies intended to accelerate R&D and the commercialization of technologies, including those that; promote the use of biochar to capture and store carbon on croplands, promote the use of wood-based materials for the construction of high-rise buildings, and promote the use of seaweed beds to capture and store CO2 (the latter being an example of the “blue carbon” concept).
In this project, which focuses on the development of promising negative emissions technologies for CO2 capture and storage anticipated in the agriculture, forestry and fisheries industries, emphasis will be placed on the promotion of ambitious R&D efforts that go beyond conventional ideas and technical limitations, targeting impactful issues that will lead to the creation of future growth industries.
Project Features
〇 Development of technologies to realize and effectively utilize high-functional biochar and other materials
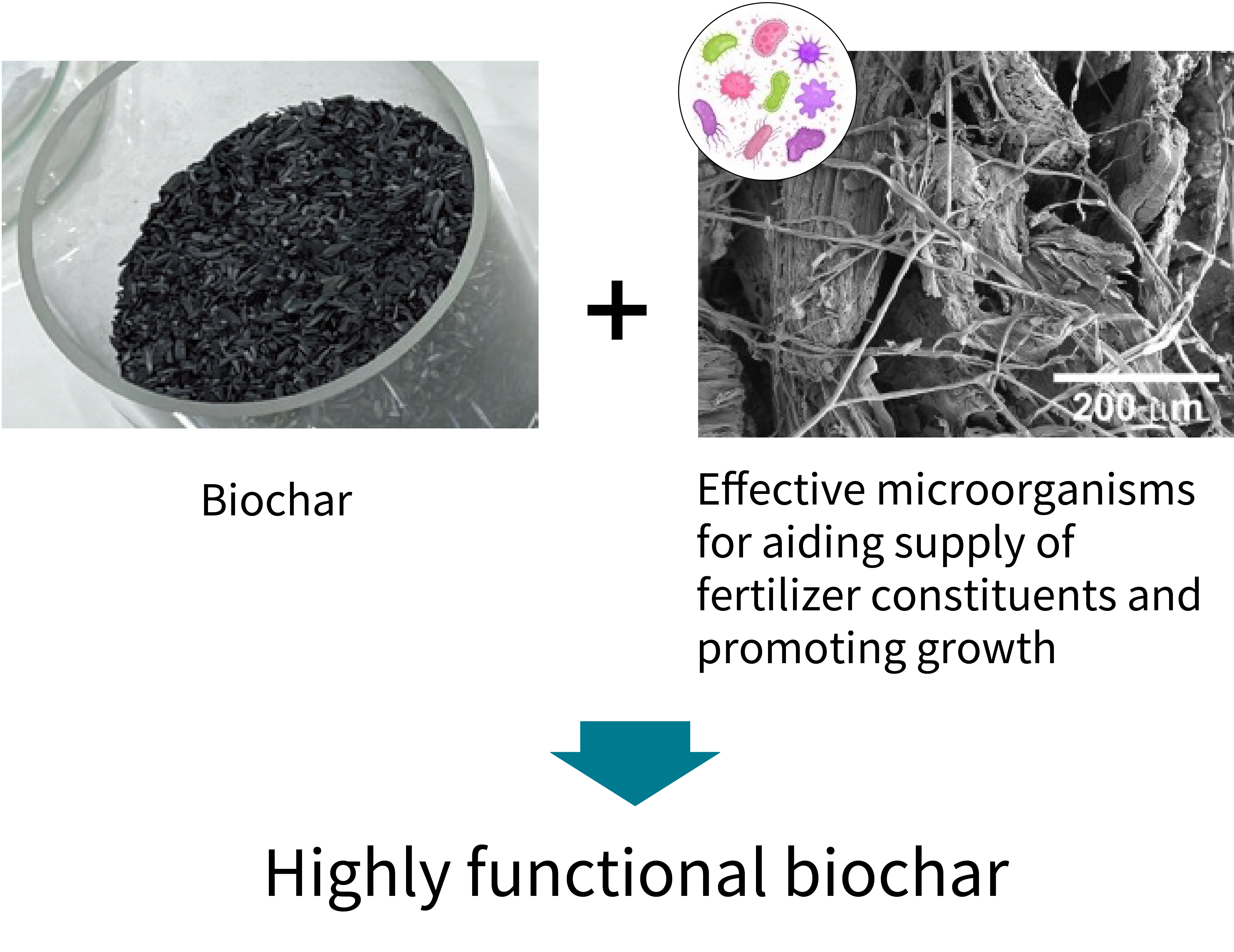
Technologies will be developed to realize and effectively utilize highly functional biochar that improves crop yields by approximately 20% and sustainably captures/stores about 3 tons of CO2 per hectare of cropland per year (equivalent to approximately 1.9 tons/hectare in terms of biochar volume). In addition, methods will be developed to objectively assess the “environmental value” of agricultural products cultivated through carbon capture and storage activities.
〇 Development of wood-based isotropic large-scale cross-sectional structural members for the construction of high-rise buildings and other structures
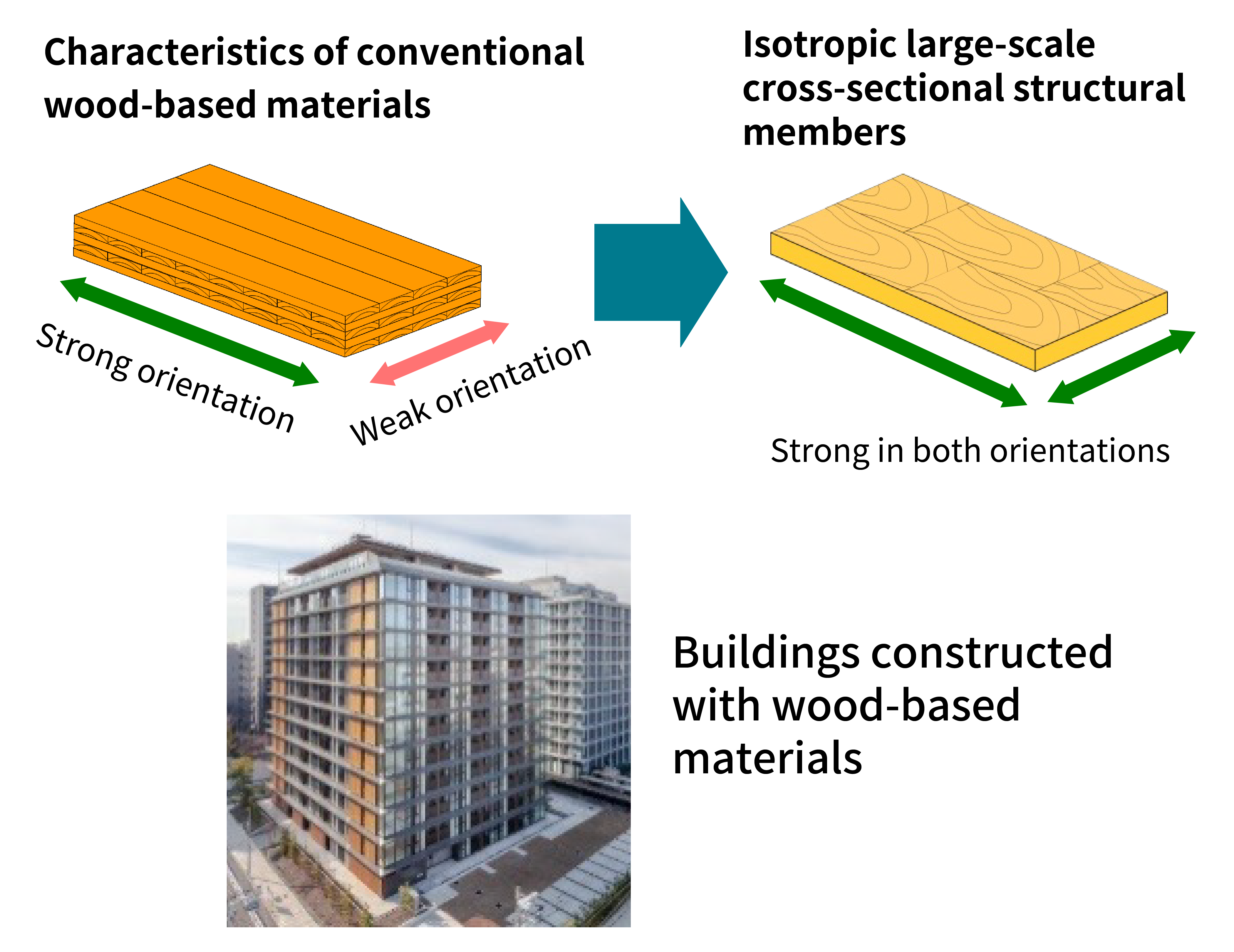
Using domestic timber resources, this project aims to develop isotropic large-scale cross-sectional structural members which possess a span of eight meters, demonstrate fire resistance for two hours, and can be manufactured at a cost of no more than 100,000 JPY per cubic meter. In addition, the project will develop proposals to establish Japanese Agricultural Standard (JAS) specifications and general design methods for such members.
〇 Development of technologies for constructing seaweed beds in support of blue carbon efforts
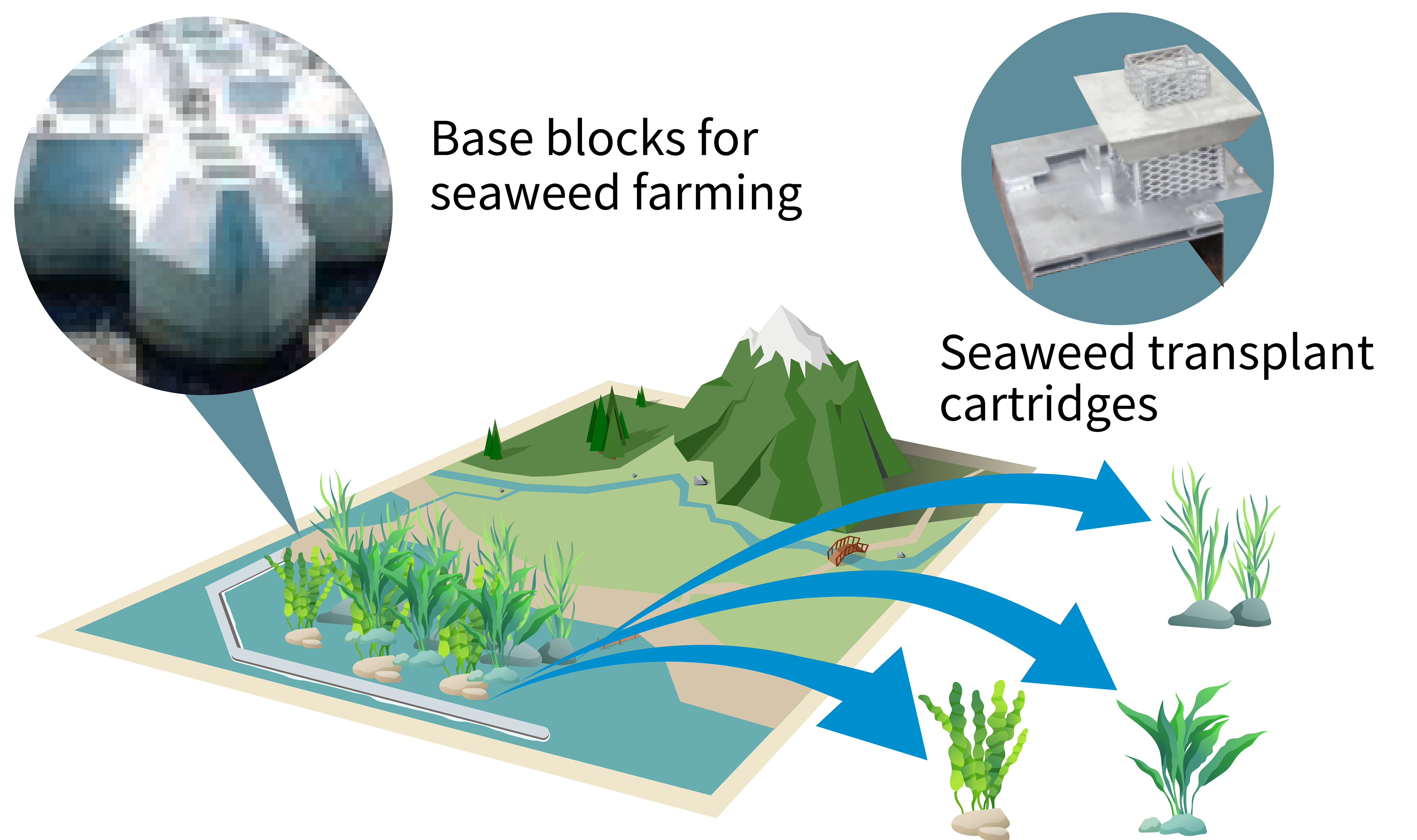
For the construction of large-scale seaweed farming systems, this project aims to develop base blocks that dissolve nutrient salts and possess a strength of 10-18 N/mm2 (the same range of strength demonstrated by conventional blocks), and seaweed transplant cartridges that weigh around 5 kg (approximately one-quarter the weight of conventional cartridges).