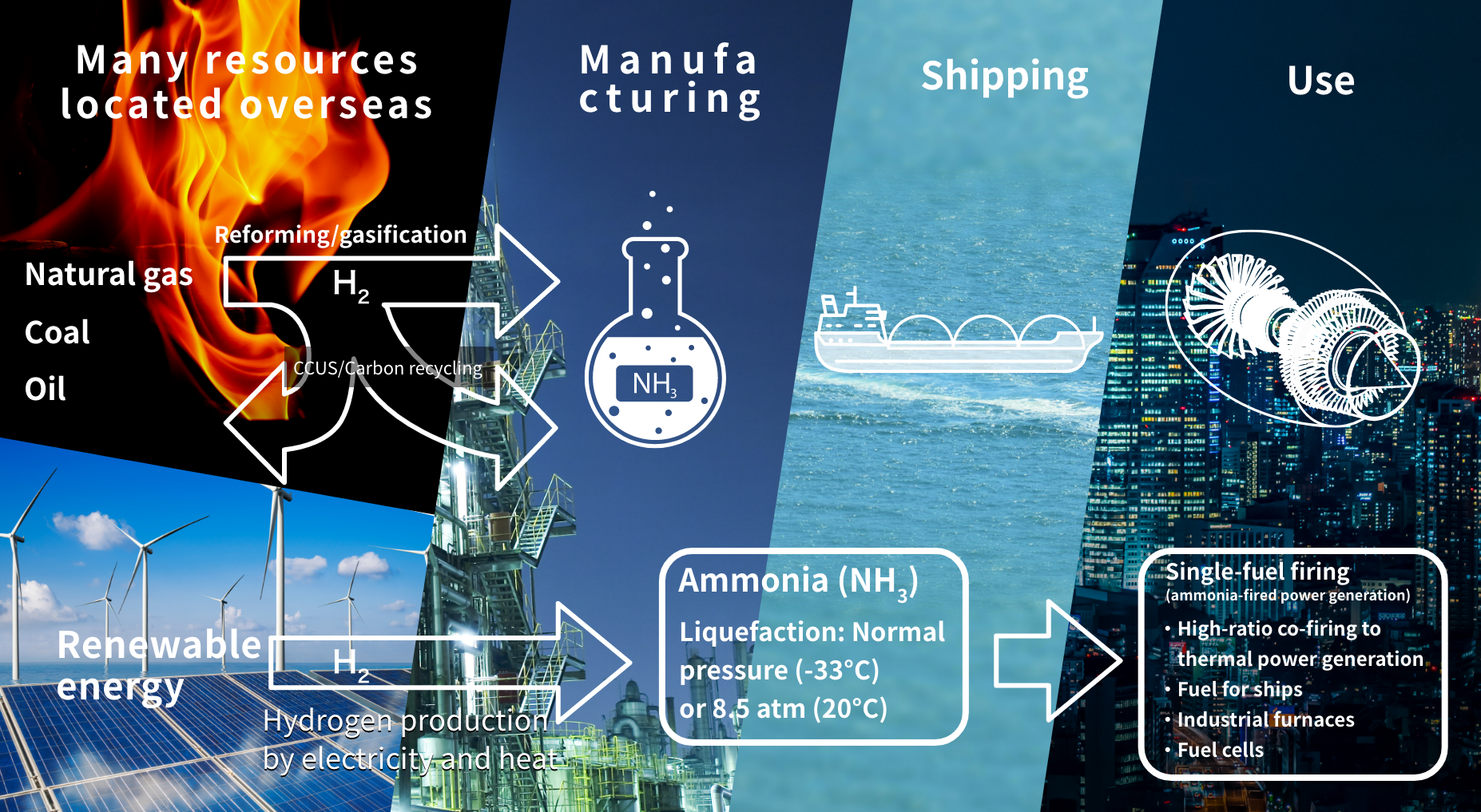
Project Summary
Budget
Up to 71.27 billion yen
CO2 Reduction Effect
- In 2030
- Approximately 6.15 million tons/year (Japan)
- In 2050
- Approximately 1,150 million tons/year (World)
Economic Effect (World)
- In 2030
- Approximately 0.75 trillion yen
- In 2050
- Approximately 7.3 trillion yen/year
Research and Development Targets
- Reduce ammonia supply costs to the high 10 yen range per Nm³ by 2030.
Develop synthetic technologies to reduce operating costs related to ammonia production by at least 15%.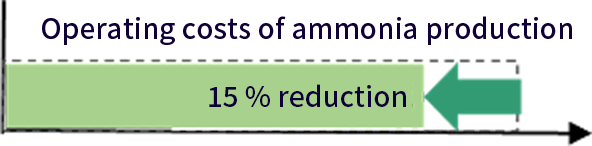 Develop green ammonia electrolysis synthesis technologies to realize production at a capacity of at least 90% of the maximum level.
Develop green ammonia electrolysis synthesis technologies to realize production at a capacity of at least 90% of the maximum level. - Develop high-ratio co-firing and single-fuel firing of ammonia technologies to realize domestic capacity goal of 30 million tons/year by 2050.
Develop technology realizing at least 50% ammonia co-firing in coal-fired power generation. Realize single-fuel firing of ammonia at actual gas turbine.
Realize single-fuel firing of ammonia at actual gas turbine.
Assumptions regarding estimates of CO2 reduction effect
- Amount of CO2 emissions that can be reduced by co-firing of 3 million tons of ammonia in coal-fired power generation in Japan in 2030.
- Amount of CO2 emissions that can be reduced by co-firing and single-fuel firing of 560 million tons of ammonia in worldwide coal-fired power generation in 2050.
Assumptions regarding estimates of economic effect
In 2030
- The cost of refurbishing facilities for co-firing operations is expected to total approximately 25 billion yen per coal-fired power generation.
- If ammonia fuel accounts for 20% of co-firing in one coal-fired power generation (1GW), approximately 0.5 million tons of ammonia fuel will be required per year.
⇒The above estimates assume utilization of 3 million tons of ammonia fuel (equivalent to 6 coal-fired power generation with 1GW capacity) in 2030 at total cost of approximately 150 billion yen (approximately 0.15 trillion yen). - The cost of building overseas terminals for ammonia fuel production and export will total approximately 200 billion yen per coal-fired power generation (1 million tons/year).
⇒The above estimate assumes supplies of 3 million tons of ammonia fuel (equivalent to 3 terminals for ammonia production and export) in 2030 at total cost of approximately 600 billion yen (approximately 0.6 trillion yen).
In 2050
- In 2050, ammonia fuel utilization will total 560 million tons. (This estimate assumes that ammonia fuel will account for 20% of global hydrogen production (550 million tons) in 2050; figure converted to ammonia tons).
- By 2050, all ammonia fuel will be used for single-fuel firing operations.
- The cost of refurbishing facilities for single-fuel firing operations will total approximately 150 billion yen per coal-fired power generation.
⇒In 2050, it is estimated the cumulative amount will be 33.6 trillion yen. - The cost of building overseas terminals for ammonia fuel production and export will total approximately 200 billion yen per plant (1 million tons/year).
⇒In 2050, it is estimated the cumulative amount will be 112 trillion yen. - From 2030 to 2050, the above figures represent the cumulative global market size. The levelized market size represents the market size for a single year.
Assumptions for realizing research and development targets
- The estimated “the high 10 yen range per Nm3 by 2030” used above in section 1, Reduction of ammonia supply costs, represents the cost of converting hydrogen assuming equivalent heat value at a price of US$3-4/MMBtu for natural gas.