
Project Overview
As of 2018, international shipping accounts for approximately 2.1% of global CO2 emissions. Since the global economy is growing, demand for shipping is expected to continue increasing and, if no action is taken, CO2 emissions from the shipping sector will also continue to increase.
To achieve carbon neutrality in the shipping sector, it is essential to move away from existing heavy oil-based fuels to gas fuels such as hydrogen, ammonia, and clean methane from recycled carbon dioxide. It is also necessary to develop shipping products that utilize hydrogen and ammonia as fuels and reduce “methane slip” on vessels fueled by LNG that contains clean methane from recycled carbon dioxide.
With the goal of realizing zero-emission ships by 2050, under this project, engines, fuel tanks, and fuel supply systems will be developed for ships using hydrogen and ammonia fuels and carry out demonstration operations using actual ships. Technology will also be developed to prevent methane slip, an important challenge for using LNG-fueled ships. The project ultimately aims to strengthen the international competitiveness of Japan's shipping-related industries, and promote social implementation in conjunction with the shipping industry.
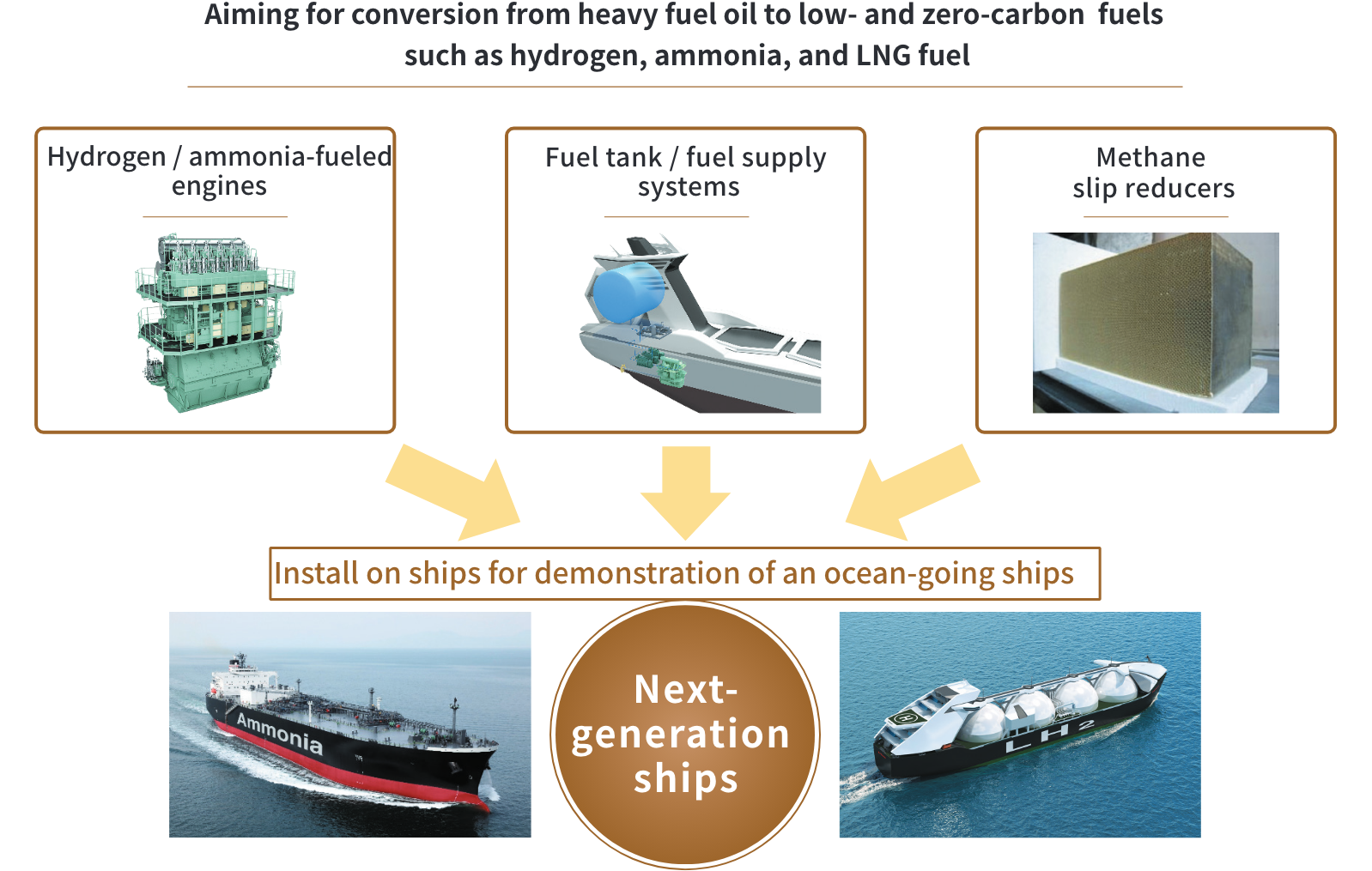
Project Features
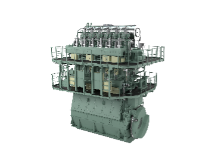
〇 Development of hydrogen-fueled ships

To achieve zero carbon emissions in the shipping industry, core technologies related to engines, fuel tanks, and fuel supply systems will be developed with the aim of realizing hydrogen-only combustion, and operational demonstrations of hydrogen fuel ships will be completed by 2030.
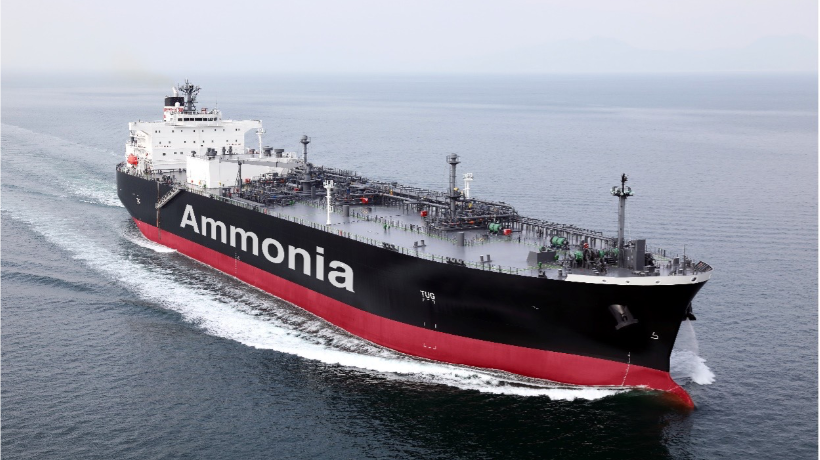
〇 Development of ammonia-fueled ships
Core technologies related to engines, fuel tanks, and fuel supply systems will be developed that utilize a high ratio of ammonia fuel to reduce greenhouse gas emissions aiming to achieve commercial operation ahead of the previous target of 2028.
〇 Preventing methane slip on LNG-fueled ships

To reduce methane emissions, which has high levels of greenhouse effect, technologies will be developed by 2026 to reduce “methane slip” levels on LNG-fueled ships by at least 60% using enhanced catalysts and engines.