
Project Overview
Steel is used in many products, ranging from spacecrafts to more common products such as automobiles, bullet trains, computers, smartphones, and houses, and the steel industry is the foundation for various other industries.
Even in the carbon-neutral society of 2050, demand is expected to remain high for automobiles and electronics as well as for products related to infrastructure. A large amount of CO2 is emitted during the manufacturing process for these products, however, and the steel industry currently accounts for 40% of CO2 emissions within the overall industrial sector in Japan.
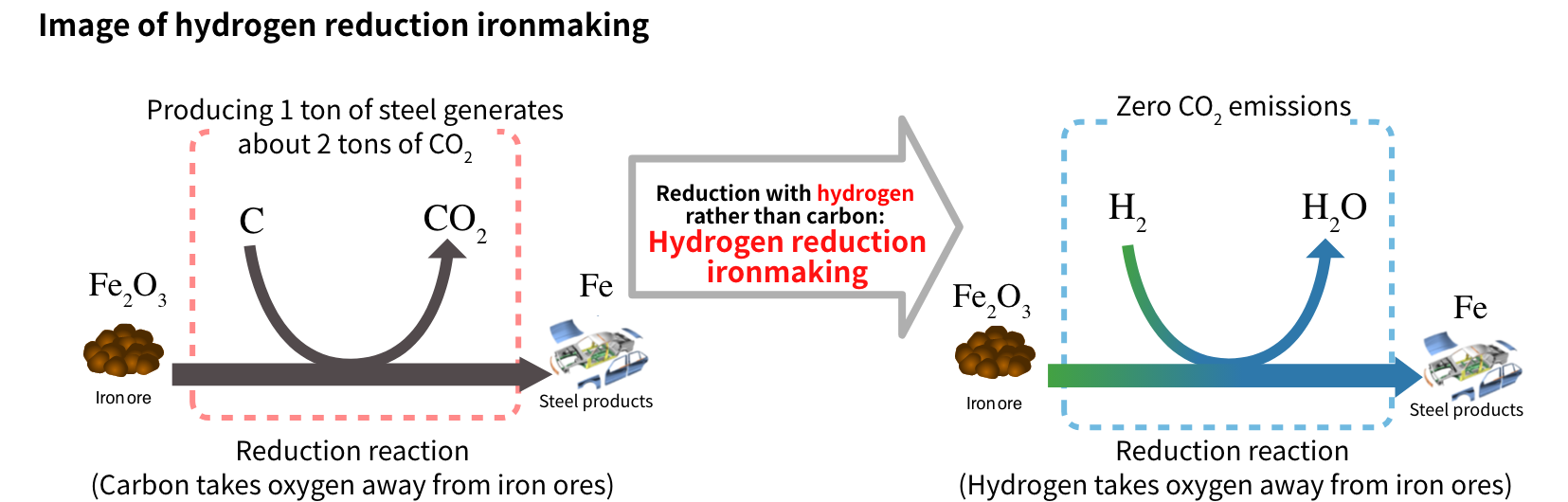
Since ancient times, the primary method for making steel has been to use carbon, in the form of charcoal or coal, as the means for reducing iron ore. However, this method inevitably generates CO2. Therefore, to reduce CO2 emissions, it is necessary to radically change the steel-making process by moving away from coal as a raw material/reduction agent. For this reason, research is underway all over the world on steelmaking through the use of hydrogen reduction where hydrogen is used instead of carbon to reduce iron ore, but this method has not yet been put into practical use.
To achieve carbon neutrality in the steelmaking process, the aim of this project is to reduce CO2 emissions by at least 50% through the application of hydrogen reduction technology to existing blast furnaces (through blast furnace hydrogen reduction technology) and technology for using hydrogen to directly reduce low-grade iron ore (through direct hydrogen reduction technology).
Project Features
〇 Development of hydrogen reduction technology using blast furnaces
Using existing blast furnace systems, hydrogen reduction technology for large-scale blast furnaces will be developed by injecting large amounts of hydrogen. Technology will also be developed that utilizes CO2 contained in blast furnace exhaust gas as a reduction agent.
〇 Development of direct hydrogen reduction technology that reduces iron ore with hydrogen only
In order to achieve the production of high-grade steel from low-grade iron ore using an integrated process with a direct hydrogen reduction furnace and an electric furnace and an integrated process with a direct hydrogen reduction furnace, an electric smelting furnace, and a converter integrated process, we will develop technology for the direct hydrogen reduction furnace and technology to control impurity concentrations in electric furnaces and electric melting furnaces to at same level as in the blast furnace method.